Solid-state drives (SSDs) have revolutionized storage, offering unmatched speed, durability, and energy efficiency compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). But when it comes to choosing the right SSD, one term throws many users for a loop: NAND flash. Deciphering the different types – SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC – can feel like cracking a code. This guide will unveil the secrets of NAND flash and help you select the perfect SSD for your unique needs.
Getting Down to the Basics
Imagine NAND flash as a microscopic grid where each cell stores data. The key difference between types lies in how many bits (0s and 1s) each cell holds.
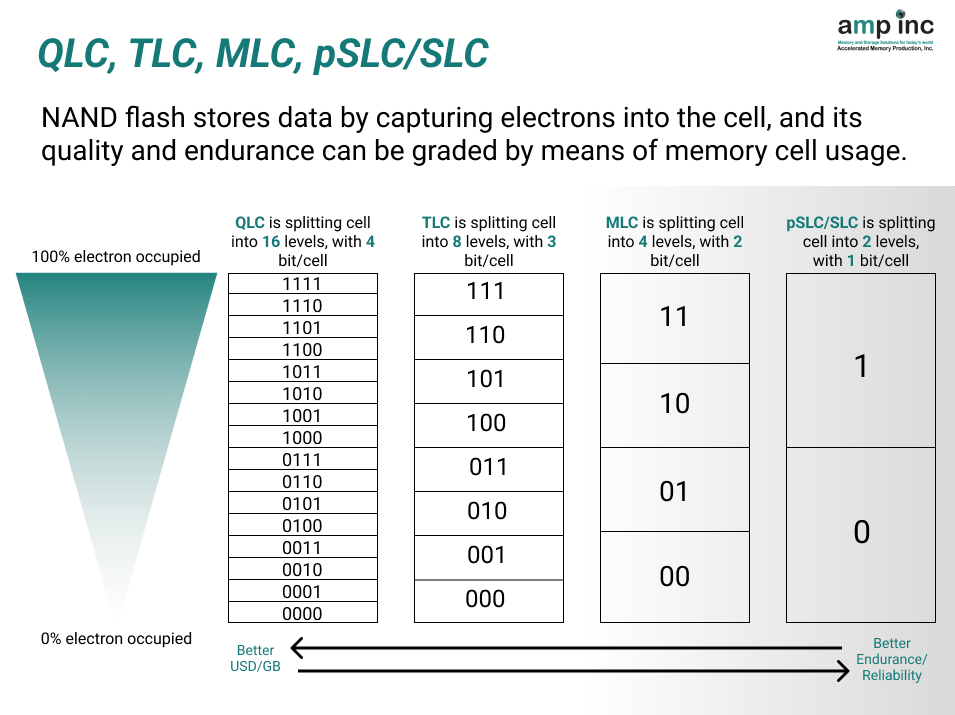
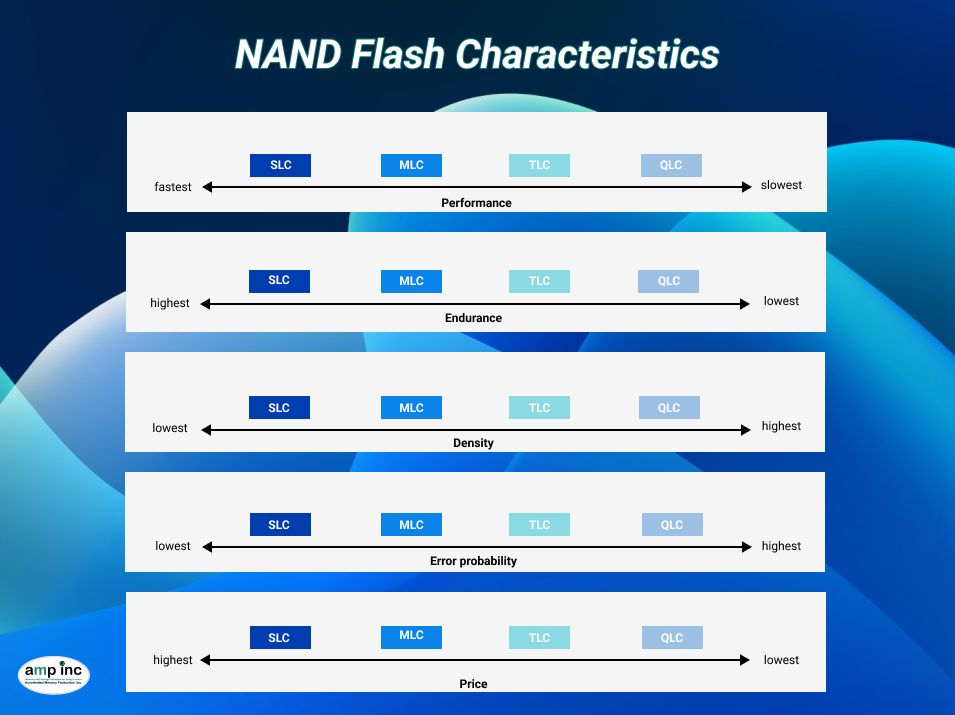
SLC (Single-Level Cell): Stores 1 bit per cell, offering the highest performance, endurance, and data integrity. Think of it as a single, brightly lit room in a library – information is easily found and protected. However, its limited density makes it the most expensive option.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell): Packs 2 bits per cell, providing a good balance of performance and affordability. Like a room with two lamps, storing more data but requiring slightly more effort to retrieve it.
TLC (Triple-Level Cell): Stores 3 bits per cell, maximizing density for budget-conscious users. Think of a room with three lamps – even higher capacity, but the retrieval process demands more complex algorithms.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell): Stores 4 bits per cell, pushing the limits of density for the most affordable option. Like a dimly lit room with four lamps – massive capacity, but data needs careful handling due to higher error rates.
Decoding Your Needs
So, which type of NAND flash is right for you? It depends on your priorities:
Heavy-Duty Performance:
Ideal: SLC or MLC
Use Case: Gamers, professionals working with large files, data centers requiring consistent speed and reliability.
Benefits: Excellent read/write speeds, high endurance (write cycles), long lifespan, superior data integrity.
Balanced Value:
Ideal: MLC or TLC
Use Case: Everyday users, casual gamers, content creators looking for a good balance between performance and cost.
Benefits: Moderate speed and endurance, decent lifespan, acceptable data integrity for most uses.
Budget-Conscious Choice:
Ideal: TLC or QLC
Use Case: Basic users, students, light gaming, browsing, storing media with lower write frequency.
Benefits: Very affordable, high capacity, suitable for static data.
Considerations: Potentially slower speeds, lower endurance, higher error rates requiring advanced wear-leveling algorithms.
Beyond the Basics
An additional development in the evolution of NAND flash worth mentioning is the introduction of 3D NAND. This innovative technology stacks layers of memory cells vertically, significantly increasing storage density compared to traditional planar (2D) NAND. This translates to higher capacities, improved endurance, and lower power consumption – all at a more competitive price point. Many modern SSDs utilize 3D NAND, offering a compelling blend of performance, affordability, and reliability for a wider range of users.
Remember, this is a simplified overview. Other factors like controller technology, DRAM cache, and form factor (SATA, NVMe) also impact performance and suitability.
Making the Smart Choice
At Accelerated Memory Production, Inc. we understand the importance of choosing the right SSD. We offer a wide range of high-quality SSDs featuring various NAND flash types to cater to diverse needs and budgets. Explore our extensive selection of SSDs and don’t hesitate to consult our expert team, we’re here to help you navigate the world of NAND flash and find the perfect SSD solution.